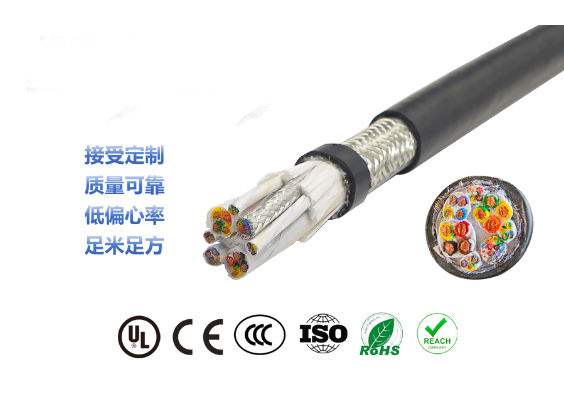
Robot Cables
Robotic Cable is a special type of cable specially designed for high-dynamic application scenarios such as industrial robots, mechanical arms, and automated equipment. It needs to meet strict requirements such as frequent bending, twisting, dragging, oil resistance, and anti-interference. The following is a detailed introduction to its core features, structure and application scenarios:
Core Characteristics of Robot Cables
1. High flexible (Dynamic Flexing) – affordable millions of times bending cycle (such as cable drag chain standard 5 million or higher). – minimum bending radius (usually 5 x cable diameter or higher).
2. Resistant to mechanical stress – 180 ° / m), tensile (such as 100 n/mm squared or higher), wear resistance (PUR sheath abrasion resistance is better than that of PVC 10 times).
3. Environmental adaptability, wide scope of heat-resistant (to 40 ℃ ~ + 90 ℃, high temperature model of up to 125 ℃). – oil resistant (ISO 1817 standard), resistance to chemical corrosion, acid and alkali solvent), resistance to UV (outdoor).
- Signal stability, high shielding effectiveness (tin plated copper wire braided coverage 85% + aluminum foil, or preventing EMI/RFI interference). – low capacitance/low latency (data cable such as EtherCAT).
Application Scenarios
1. Industrial robots – mechanical arm joint wiring three-dimensional movement (tolerance). – welding torch cable (high temperature resistance welding slag, such as silicone rubber sheath).
2. Automatic equipment – drag chain system (numerical control machine tools, logistics sorting line). – servo motor power cable + encoder signal integration.
3. The special environment – clean room (without silicon low dust), food grade (FDA certification sheath). – explosion-proof occasions (flame retardant IEC 60332-1).
Key indicators for selection
1.The dynamic performance – bending radius (e.g., 4 x D), (+ 180 ° / m), torsion Angle acceleration (10 m/s squared) or higher.
2. Electrical parameters – the voltage level (300 v / 500 v), insulation resistance (100 m or higher Ω km). – the signal transmission rate (such as 1 gb/s @ 100 MHZ).
3. Certification standards – UL/CE, RoHS, REACH (environmental protection), TUV (safety certification).
Frequently asked question
-Q: Why are robot cables prone to damage? – > sheath material improperly, such as PVC hardening cracking or bending radius is too small (< design value). Q: and what is the difference between ordinary cable? – more than ordinary cable for the static laying cable robot by dynamic testing (e.g., drag chain test, distortion test).
Maintenance recommendation
Avoid overload (current ≤ 80% of the nominal value). – periodic inspection sheath wear (especially internal drag chain). – use a dedicated cable guide (lower mechanical stress). Robots are the automated production cable “nerves and blood vessels,” selection error may lead to signal packet loss or equipment downtime. It needs to be comprehensively matched based on the form of movement, environment and electrical requirements!
|
Structural |
materials and techniques |
function |
|
Conductor |
Tin-plated copper wire (0.05-0.1mm fine wire, twisted in multiple strands) |
High electrical conductivity + antioxidant |
|
Insulation |
TPE、TPU、FEP、silicone rubber |
Elastic recovery + heat resistance |
|
Filling |
Aramid fiber /PP rope |
Tensile strength + maintaining roundness |
|
Shield |
Tin-plated copper wire braided + aluminum foil composite |
Anti-electromagnetic interference (CAT6 level) |
|
Jacket |
PUR、TPU、PVC |
Wear-resistant, oil-resistant and low adhesion |